In 1955, the U.S. Air Force began its Weapons
System program for the development of a strategic satellite system. The
initial primary goal was the development an orbital photo-reconnaissance
platform, and in October 1956, Lockheed became prime contractor for the
system. The core element was a new multipurpose spacecraft with boost
and manoeuvering engines, which would act as the second stage of the launch
vehicle as well as the carrier vehicle for the reconnaissance system.
Lockheed's Agena spacecraft was built around the Bell XLR-81 liquid-propellant
rocket engine, and was initially known informally as Hustler, because
the XLR-81 was originally developed for a rocket-powered weapons pod for
the B-58 Hustler bomber.
The first launch of a Thor-Agena combination in January 1959 was a failure,
but on 28 February that year, Agena scored its first success when a Thor-Agena
launcher placed the Discoverer 1 satellite into polar orbit.
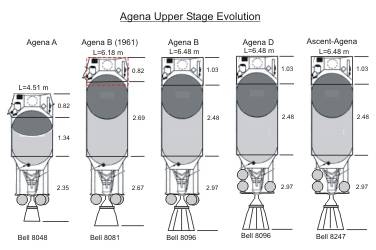
The Agena space vehicle was used in large numbers during the 1960s and
1980s as upper stage with Thor, Atlas and Titan-3 boosters to launch
a variety of military and civilian payloads into orbit. The Agena itself
was actually the first general-purpose satellite, and formed the core
for many operational satellites and experimental space vehicles. It is
included in this missile directory, because the U.S. Air Force allocated
the formal missile designator RM-81 to the Agena. |
|
The first few Agenas, including the vehicle used in the Discoverer-1 launch,
used a Bell XLR-81-BA-3 rocket engine, but most vehicles of the initial Agena
A series used an XLR-81-BA-5 (Bell Model 8048). The engine had gimballed nozzles
for pitch and yaw control. The engine was notable for its unusual aluminum
construction. The regeneratively-cooled channels that cooled the throat and
nozzle were formed from straight gun drill formed channels.
Specification
Propellant: IRFNA/UDMH
Propellant mass: 3,055 kg
Propellant mix rate: 2.55
Engine: Bell 8048 (XLR-81-BA-5)
Area ratio: 20
Thrust: 68.9 kN (15,489 lbf)
Chamber pressure: ?
Specific impulse: 276 sec
Flow rate: 25.46 kg/sec
Burn time: 120 s
Launches: 18
(Two early vehicles have used the engine Bell 8001) |

Combustor
|

Bell 8048
|
|
Launch Vehicle
|
Launches
|
Payload
|
Time
|
|
Atlas LV3
|
4
|
Midas, Samos
|
26.02.1960 - 31.01.1961
|
|
Thor
|
DM-18
|
14
|
Discoverer
|
13.04.1959 - 13.09.1960
|
The Agena B had an improved XLR-81-BA engine , which could be restarted in
space, and was stretched to carry much more propellant, doubling the total
burn time to 240 s. The engine Bell 8081 has a modified combustor with a flanged
and extended nozzle.
Specification
Propellant: IRFNA/UDMH
Propellant mass: 6,112 kg
O/F mix rate: 2.57
Engine: Bell 8081 (XLR-81-BA-7)
Area ratio: <45
Thrust: 70.7 kN (15,890 lbf)
Chamber pressure: ?
Specific impulse: 283 sec
Flow rate: 25.47 kg/sec
Burn time: 240 s
Launches: 33 |
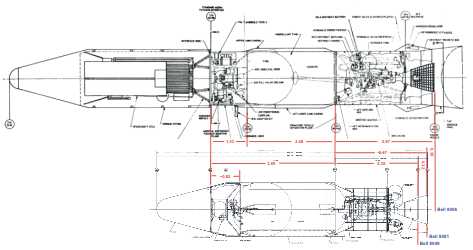
Agena-D (above) and Agena-B
|

Bell 8081 (rare image)
|
|
Launch Vehicle
|
Launches
|
Payload
|
Time
|
|
Atlas LV3
|
3 |
Midas 3, 4, 5
|
12.07.1961 - 09.04.1962
|
| 4 |
Samos (Sentry)
|
22.11.1961 - 07.03.1962 |
| 4 |
Ranger 1, 2, 3, 4
|
23.08.1961 - 23.04.1962 |
|
Thor
|
DM-21
|
2
|
RM-1, RM-2
|
20.12.1960 - 18.02.1961
|
|
16
|
Corona (KH-2, KH-3
|
26.10.1960 - 13.01.1962
|
| 4 |
Argon (KH-5)
|
17.02.1961 - 21.07.1961 |
The Agena D variant was essentially a "standardized" Agena B, which could
accept a variety of payloads. Both used the new engine Bell 8096 with a 30
cm extended nozzle and surface structure.
Later, the Agena-D was filled with the new fuel combination HDA/UDMH, what
has improves the performance of the engine Bell 8096-39.
Specification (1)
Propellant: IRFNA/UDMH
Propellant mass: 6,112 kg
O/F mix rate: 2.57
Engine: Bell 8096 (XLR-81-BA-11)
Area ratio: > 45
Thrust: 71.2 kN (16,006 lbf)
Chamber pressure: 506 psia
Specific impulse: 291 sec
Flow rate: 24.95 kg/sec
Burn time: 245 s
Launches: 270 |
Specification (2)
Propellant: HDA/UDMH
Propellant mass: 6,143 kg
O/F mix rate: 2.69
Engine: Bell 8096-39
Area ratio: > 45
Thrust: 75.3 kN (16,930 lbf)
Chamber pressure: ?
Specific impulse: 300 sec
Flow rate: 25.60 kg/sec
Burn time: 240 s
Launches: 19 (KH-8 ?) |
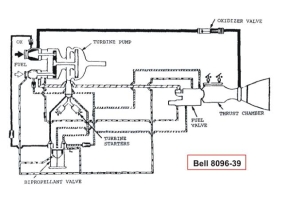
Bell 8096-39 flow diagram
|

Bell 8096
|
|
Agena-B (41)
|
Launch Vehicle
|
Launches
|
Payload
|
Time
|
|
Atlas LV3
|
4
|
Midas
|
17.12.1962 - 19.07.1963 |
| 5 |
Samos (Corona)
|
26.04.1962 - 11.11.1962 |
| 5 |
Ranger-5 to 9
|
18.10.1962 - 21.03.1965 |
| 2 |
Mariner-1, 2
|
22.07.1962, 27.08.1962 |
| 1 |
OGO-1
|
05.09.1964 |
|
Atlas SLV3
|
1
|
OGO-3
|
07.06.1966
|
|
Thor
|
DM-21
|
11
|
Corona (KH-4)
|
27.02.1962 - 24.11.1962
|
| 3 |
Argon (KH-5)
|
15.05.1962 - 09.10.1962 |
|
Thor
|
DM-21
|
3 |
Samos-F2
|
21.02. 1962 - 16.01.1963 |
| 2 |
Alouette (2)
(+Expl.-31)
|
29.09.1962, 29.11.1965 |
| 1 |
Echo-2
|
25.01.1964 |
| 1 |
Nimbus-1
|
28.08.1964 |
|
TAT
|
SLV-3A
|
2 |
OPS 1440, Nimbus-2
|
29.06.1963, 15.5.1966 |
|
Agena-D
(248)
|
Launch Vehicle
|
Launches
|
Payload
|
Time
|
|
Atlas LV3
|
10
|
Gambit (KH-7)
|
12.07.1963 - 23.10.1964
|
|
Atlas SLV3
|
28
|
Gambit (KH-7)
|
14.08.1964 - 04.06.1967
|
|
Atlas SLV3
|
18
|
diverse
|
17.10.1963 - 05.11.1967
|
|
Atlas SLV3A
|
12
|
OPS, OGO-5
|
04.03.1968 - 07.04.1978
|
|
Atlas-F
|
1 |
SEASAT
|
27.06.1978
|
| Atlas
SLV3mod |
1 |
OAO-1
|
08.04.1966 |
|
Thor
|
DM-21
|
14
|
KH-4 (12), KH-5 (2)
|
28.06.1962 - 28.09.1963
|
|
Thor
|
8
|
diverse
|
26.10.1962 - 31.05.1967
|
|
TAT
|
SLV-2A
|
41
|
KH-4 (3), KH-4A (38)
|
28.02.1963 - 30.03.1967
|
|
TAT
|
6
|
KH-5 (3), KH-6 (3)
|
18.03.1963 - 21.08.1964
|
| TAT |
13 |
diverse |
11.01.1964 - 17.01.1968 |
|
Thorad
|
SLV-2G
|
20
|
KH-4A (13), KH-4B (7)
|
09.08.1966 - 22.09.1969
|
|
Thorad
|
10 |
diverse
|
18.05.1968 - 14.12.1971 |
|
Thorad
|
SLV-2H
|
11
|
KH-4B
|
24.07.1969 - 25.05.1972
|
|
Thorad
|
2 |
OGO-6, OPS 8373
|
05.06.1969, 16.07.1971 |
|
Titan-3B
|
29
|
Gambit (KH-8)
|
29.07.1966 - 23.10.1970
|
|
Titan-3B+
|
23B
|
2
|
Gambit (KH-8)
|
21.01.1971, 22.04.1971
|
|
Titan-3BS
|
24B
|
22
|
Gambit (KH-8)
|
12.08.1971 - 17.04.1984
|
|
A modified Bell 8096 engine used first time for NASA’s Project Gemini.
This Bell 8247 engine had a modified starting system, propellant valves and
different electrical controls. The changes gave it repeated multiple restarts.
With a high probability the engine Bell 8247 later was used for the "Ascent
Agena", which was used from 1971 to 1987 for the launch of geostationary
satellites Jumpseat and SDS with the Titan-3B and -2BS (mod).
|
Specification
Propellant: IRFNA/UDMH
Propellant mass: 6,112 kg
O/F mix rate: 2.57
Engine: Bell 8247 (XLR-81-BA-13)
Area ratio: > 45
Thrust: 71.7 kN (16,115 lbf)
Chamber pressure: ?
Specific impulse: 293 s
Flow rate: 24.95 kg/sec
Burn time: 245 s
Launches: 20
|
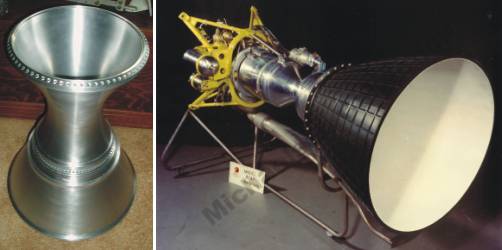
Bell 8247
|
|
|
Launch Vehicle
|
Launches
|
Payload
|
Time
|
|
Atlas SLV3
|
6
|
GATV
|
25.10.1965 - 11.11.1966
|
|
Titan-3B mod
|
33B
|
3
|
Jumpseat
|
21.03.1971 - 21.08.1973
|
|
Titan-3BS mod
|
34B
|
11
|
Jumpseat, SDS
|
10.03.1975 - 12.02.1987
|
|